Geography Class 11
Last class revision(5.10 PM).
Isostatcy/Isostatic movements(5.22 PM):
- Isostasy is the state of equilibrium or balance in the earth's crust.
- Isostatic movements involve vertical movements under the action of floatation displacement between the rock layers of differing density and mobility.
- This is to achieve balanced crustal columns of uniform mass above a level of compensation in which the topographic elevation is inversely related to underlying rock density.
- For example, the Mountains have deep roots, like the Scandinavian mountains due to the melting of ice sheets are observing the gradual rising of the land which is evident in a series of raised beaches.
Eustatic movements(5.44 PM):
- They involve the worldwide movement of sea level resulting from changes in the total volume of liquid seawater or capacity of ocean basins.
- The volume of seawater can be changed by melting or the formation of glaciers.
- The capacity of the basin can be changed through the formation of ridges or the expansion of basins.
Continental drift theory(5.55 PM):
- The continental drift theory was proposed by Alfred Wegner(a german meteorologist) in 1912.
- The theory was proposed to explain major variations in the earth's climate.
- Assumptions:
- The three layers of the earth with outer SiAl, intermediate SiMa, and inner NiFe.
- The continental masses were assumed to be floating on oceanic crust without any resistance.
- The Theory:
- Before the Carboniferous period(280-250 million years ago), there was only one supercontinent called Pangea and one superocean called Panthalassa.
- This Supercontinent started to rift during the Carboniferous period.
- It was split into northern Angaraland(Laurasia) and southern Gondwanaland by a rift running east to west.
- Gradually this rift enlarged to form the Tethys Sea.
- The Angaraland consisted of North America, Greenland, and Eurasia without India and Arabia.
- The southern Gondwanaland consisted of Africa, South America, India, Australia, and Antarctica.
- A North-South rift separated North America from Eurasia and South America from Africa which started to move towards the West.
- India started moving toward the North.
- Australia got separated from Antarctica and moved toward the northeast
- Africa moved towards the north.
- Finally, Arabia got separated from Africa and merged into Asia.
- Forces responsible for the continental drift:
- Alfred Wegner proposed the following forces as the cause of continental motion:
- Equatorward or North-South movement is caused by the Pole-fleeing force due to Gravitational differential force and the force of Buoyancy.
- The westward movement is caused by the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon.
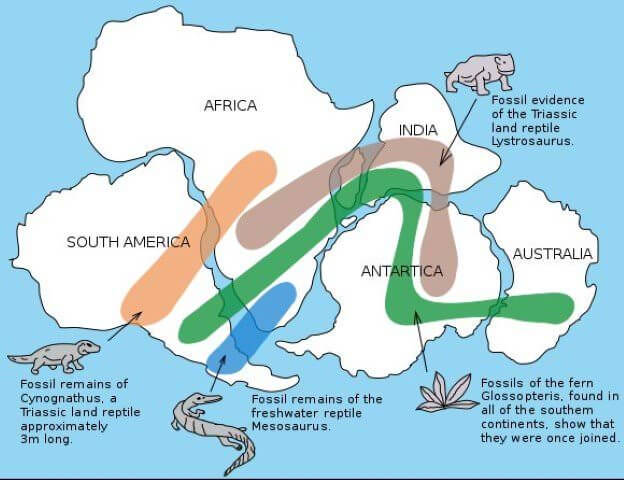
Evidence in support of continental drift theory(7.12 PM):
- The diagrammatic representation of pieces of evidence:
-
- Justafix or zig-saw fits of continents:
- There are similarities in coastlines on opposite sides of the Oceans.
- All the continents can be merged to form one big continent.
- Structural pieces of evidence:
- The nature of physiography structure in different parts of the continents, having the same age and structural properties
- The mountain belts of Brazil terminate on the South American east coast and the same type of mountains reappeared again in Africa.
- Stratigraphic pieces of evidence:
- The eastern coast of brazil has the same type of rock formations observed along with Northwest Africa.
- Fossil evidence:
- Mosasaurus is an aquatic reptile whose fossil remains are found only in South America and South Africa separated by a wide ocean.
- The fossils of Glossopteeris(a fern) grown only in subpolar climates are now found in warm climatic regions separated by wide Oceans.
- Glacial deposits:
- The layers of tillites are found in warm tropical regions like South America, South Africa, Australia, and India.
- Placer deposits:
- The rich deposits of gold Placer near the Ghana coast without any source of Gold nearby.
Criticisms of continental drift theory(7.44):
- The forces suggested for the movement of the continent are considered to be inadequate.
- The rocks of continental crust and oceanic crust are very rigid and would not permit the drifting of continents over the oceanic floor.
- The theory did not describe the situations of pre-carboniferous times.
Mapping(7.49 PM):
- Africa:
- It is also called the dark continent as it was discovered very late.
- It is home to the largest desert(the Sahara desert).
- It is home to the longest river on the earth that is the Nile river.
- The Nile is made of 2 rivers, the blue and white Nile.
- Mount Kilimanjaro is the highest point in Africa.
- The lowest point in Africa is the lake Assal(in Djibouti).
The topic for the next class: Seafloor spreading and plate tectonic theory.